

A polygon is drawn as a set of ordered vertices relative to the shape's x,y coordinate.
The following contains an example that will add a star polygon to a canvas. The blue lines represent the x and y axes, and show through since an alpha value of 0.9 is used.
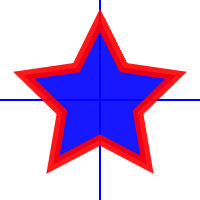
Star shaped polygon drawn by example code below
void add_polygon_star( Papyrus::Canvas::pointer canvas ) { // Create a filled polygon that will form a star Papyrus::Polygon::pointer polygon = Papyrus::Polygon::create(); // Add the polygon to the canvas canvas->add( polygon ); // Set the fill color to red, with an alpha value of 0.9 polygon->set_fill( Papyrus::RGBA(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.9) ); // To color the lines of a polygon shape, set the stroke paint polygon->set_stroke( Papyrus::RGBA(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.9) ); // Set a line width polygon->stroke()->set_width(10); // Add the 10 points of the star for (double angle=-M_PI_2; angle < 1.5*M_PI; angle += M_PI/2.5) { polygon->add_vertex( cos(angle)*80, sin(angle)*80); polygon->add_vertex( cos(angle+M_PI/5.0)*40, sin(angle+M_PI/5.0)*40); }
Note that the major difference between a polygon and a polyline is that a polygon will close the surface on the stroke, while a polyline will not. Below is the image generated from a polyline with vertices in the shape of a U, and following is a polygon with the same vertices.

Filled Polyline with U vertices
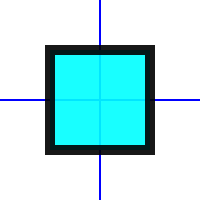
Polygon with U vertices
void add_polygon_u( Papyrus::Canvas::pointer canvas ) { // Create a filled polygon that will form a U Papyrus::Polygon::pointer polygon = Papyrus::Polygon::create(); // Add the polygon to the canvas canvas->add( polygon ); // Set the fill color to red, with an alpha value of 0.9 polygon->set_fill( Papyrus::RGBA(0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.9) ); // To color the lines of a polygon shape, set the stroke paint polygon->set_stroke( Papyrus::RGBA(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.9) ); // Set a line width polygon->stroke()->set_width(10); // Add the four points of the U (upper left, lower left, lower right, upper right) polygon->add_vertex( -50, -50 ); polygon->add_vertex( -50, 50 ); polygon->add_vertex( 50, 50 ); polygon->add_vertex( 50, -50 ); }
 1.6.1
1.6.1